Archaeopteryx


ARCHAEOPTERYX
Archaeopteryx lived during the Late Jurassic period, approximately 150 million years ago. It shared its environment with other famous dinosaurs like Allosaurus and Diplodocus. The Solnhofen Limestone where its fossils are found preserved exceptional details due to its fine-grained nature and lack of oxygen, which aided in the preservation of delicate features like feathers.
SIZE AND ANATOMY
- Feathers: Archaeopteryx had feathers covering its body, wings, and tail. These feathers were similar to those of modern birds, suggesting it was capable of powered flight.
- Reptilian Features: It retained many reptilian features, such as a long bony tail, clawed fingers on its wings, and teeth in its beak-like jaws.
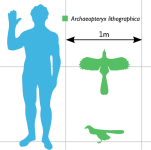
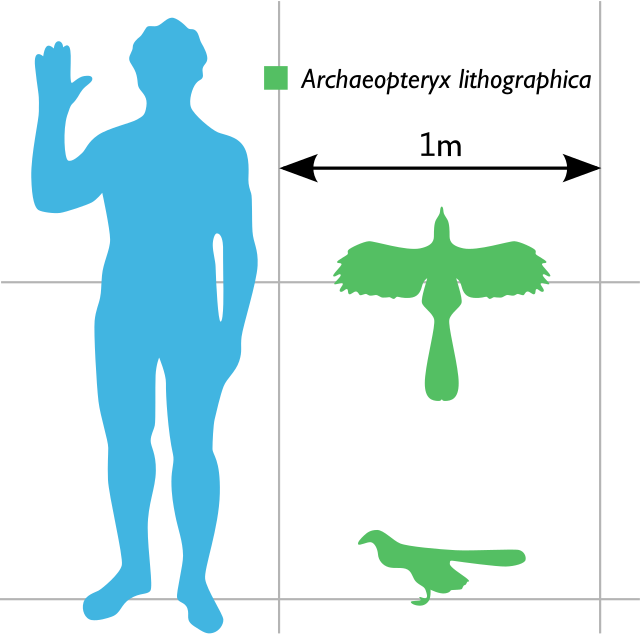
- Size: Archaeopteryx was about the size of a raven, with an estimated length of around 0.5 to 0.6 meters (1.6 to 2 feet).
BEHAVIOR AND ECOLOGY
- Transitional Nature: Archaeopteryx is considered a critical transitional fossil because it shares both avian and dinosaurian characteristics. It provides evidence supporting the theory of evolution by natural selection and the origin of birds from theropod dinosaurs.
- Flight Capability: The presence of feathers and wing structures in Archaeopteryx suggests it was capable of powered flight, although its flight abilities may have been more limited compared to modern birds.
- Paleoecology: Archaeopteryx lived in a coastal or island environment during the Jurassic period, where it likely fed on small vertebrates, insects, and possibly plants.
FOSSILS AND DISCOVERY:
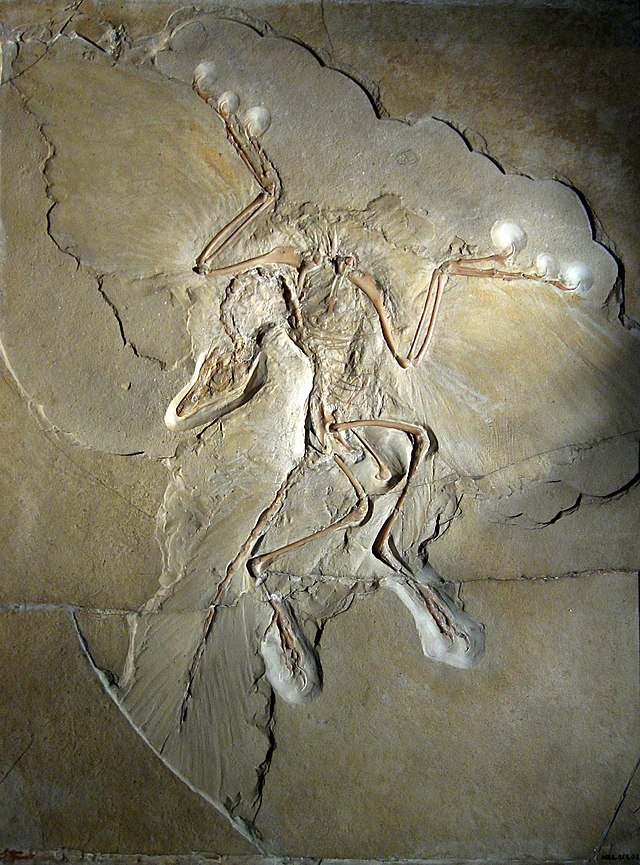
- Archaeopteryx, meaning “ancient wing” in Greek, is a genus of bird-like dinosaur that lived during the Late Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. The first fossil was discovered in Germany in 1861, just two years after Charles Darwin published “On the Origin of Species,” making Archaeopteryx a pivotal discovery in the study of evolution.
CLASSIFICATION
- Kingdom: Animalia – Archaeopteryx belongs to the kingdom Animalia, as it is a multicellular, eukaryotic organism.
- Phylum: Chordata – Archaeopteryx is classified under the phylum Chordata, as it possesses a dorsal nerve cord, notochord (at least in early development), pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail at some point in its life cycle.
- Class: Aves – Archaeopteryx is classified under the class Aves, which includes all modern birds. Despite its dinosaurian features, it is considered an early bird due to its feathered wings and flight adaptations.
- Order: †Archaeopterygiformes – Archaeopteryx is placed within the order Archaeopterygiformes, which is an extinct order of birds that includes only Archaeopteryx.
- Family: †Archaeopterygidae – Within the order Archaeopterygiformes, Archaeopteryx belongs to the family Archaeopterygidae. This family includes only the genus Archaeopteryx.
- Genus: Archaeopteryx – Archaeopteryx is the genus name, referring specifically to this ancient bird-like dinosaur.
- Species: Archaeopteryx lithographica – There is only one recognized species within the genus Archaeopteryx, which is Archaeopteryx lithographica. The specific epithet “lithographica” refers to the lithographic limestone where the first fossils were found.
FUN FACTS:
- Feathered Dinosaur: Archaeopteryx is one of the earliest known dinosaurs to have feathers. Its feathers were similar in structure to modern bird feathers, indicating that it had a covering of feathers across its body, wings, and tail.
- First Bird: Archaeopteryx is often referred to as one of the first birds, although it retains many characteristics of its dinosaurian ancestors, such as teeth, a long bony tail, and clawed fingers on its wings. Its discovery helped support the hypothesis that birds evolved from theropod dinosaurs.
- Flight Capabilities: While Archaeopteryx had feathers and wings capable of flight, its flight capabilities are still debated among scientists. It likely had some ability for powered flight, but it may have been more suited for gliding or short bursts of flight.
- Rare Fossils: Fossils of Archaeopteryx are exceptionally rare and highly valuable. Only a handful of well-preserved specimens have been discovered, all from the Late Jurassic Solnhofen limestone deposits in Germany. These fossils provide important insights into the evolution of birds and the transition from dinosaurs to avian species.