Triceratops

TRICERATOPS
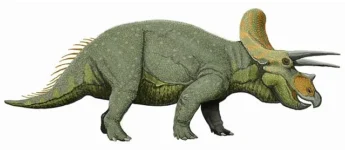
Triceratops was a large herbivorous dinosaur that lived during the late Cretaceous period, approximately 68 to 66 million years ago. Triceratops is one of the most iconic dinosaurs, providing significant insights into the diversity and evolution of ceratopsians. Its well-preserved fossils help paleontologists understand the anatomy, behavior, and environment of late Cretaceous herbivores.
Here are some key details about Triceratops:
SIZE AND ANATOMY:
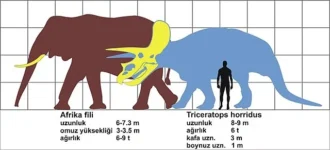
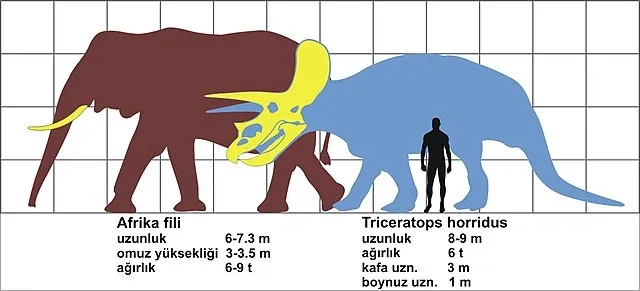
- Size: Triceratops grew up to about 30 feet (9 meters) in length and stood about 10 feet (3 meters) tall at the hips.
- Weight: It weighed between 6 to 12 tons.
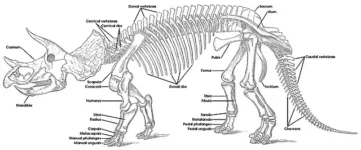
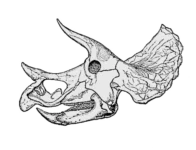
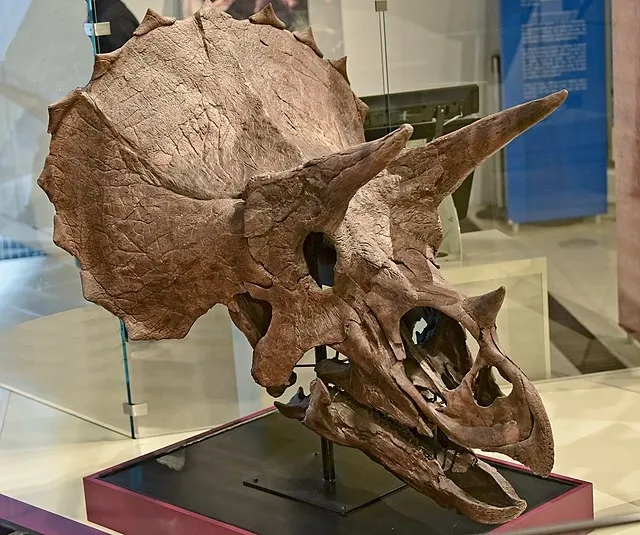
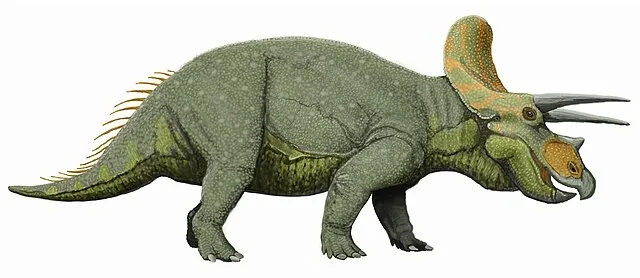
- Skull and Horns: Triceratops had a massive skull that could be up to one-third of its body length. It featured three distinct facial horns: two long ones above the eyes and a shorter one on the nose. It also had a large bony frill at the back of the head.
- Limbs: It had sturdy, column-like legs to support its massive body, with the front limbs being shorter than the hind limbs.
CLASSIFICATION
- Order: Ornithischia
- Suborder: Marginocephalia
- Family: Ceratopsidae
- Genus: Triceratops
- Species: The most well-known species are Triceratops horridus and Triceratops prorsus.
FOSSILS AND DISCOVERY:
- First Discovery: The first Triceratops fossil was discovered in 1887 by John Bell Hatcher in the Denver Formation of Colorado, USA. It was named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1889.
- Significant Finds: Numerous Triceratops fossils have been found across the western United States, especially in the Hell Creek Formation, making it one of the best-represented dinosaurs in the fossil record.
BEHAVIOR AND ADAPTATIONS:
- Diet: Triceratops was an herbivore, feeding on low-growing vegetation such as ferns, cycads, and palms. Its beak-like mouth and rows of cheek teeth were adapted for cutting and grinding plant material.
- Social Behavior: There is some debate about whether Triceratops lived in herds or was more solitary. Evidence from fossil sites suggests they might have had complex social behaviors, possibly including group defense against predators.
- Habitat: Triceratops lived in what is now North America, particularly in regions that were part of the Western Interior Seaway, which included floodplains, forests, and coastal areas.
FUN FACTS:
- Frill and Horns: The purpose of the frill and horns of Triceratops has been widely debated. They may have been used for defense against predators, species recognition, and social interactions such as mating displays and dominance contests.
- Strong Bite: Despite being an herbivore, Triceratops had one of the most powerful bites of any land animal, thanks to its robust jaws and rows of teeth that could exert significant force to process tough plant material.
- Bone Bed Discoveries: Fossil evidence, including bone beds with multiple individuals, suggests that Triceratops may have occasionally lived in groups, which could have provided protection against predators.
- Misidentified Relatives: For a long time, paleontologists thought Triceratops might be the same as another ceratopsian dinosaur called Torosaurus. However, further studies have suggested that they are distinct genera, with differences in their frill structure and skull morphology.avily armored appearance gave it a unique and formidable presence among Late Cretaceous dinosaurs.