AMBER
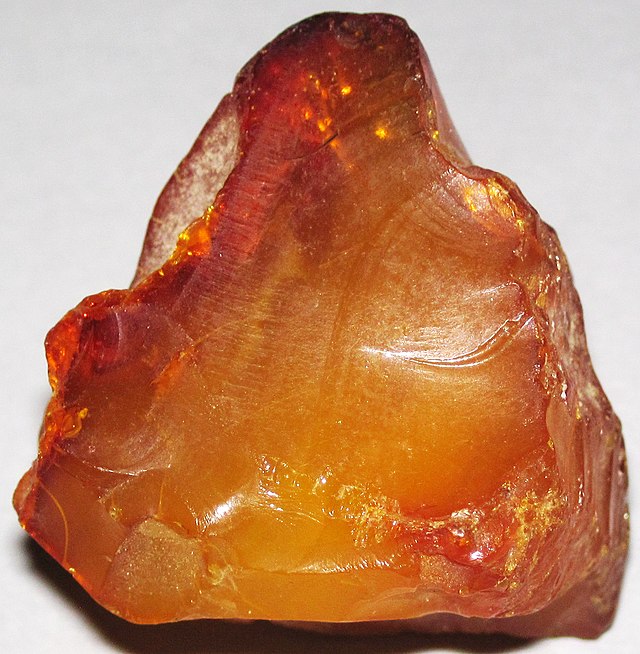
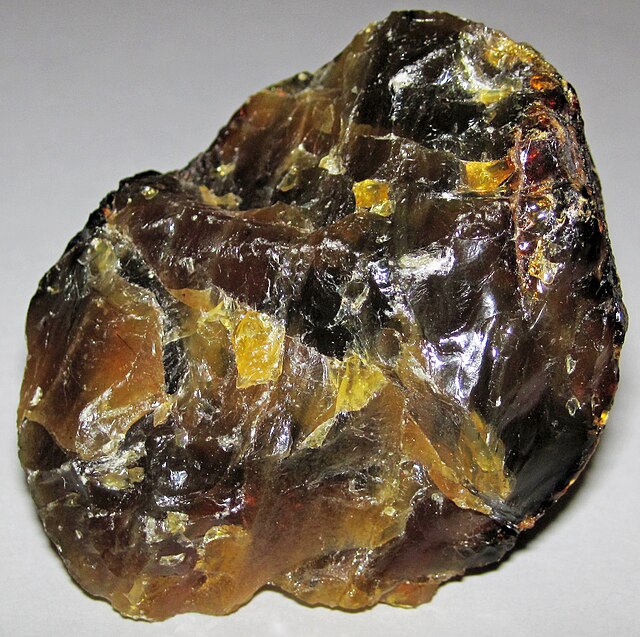



Amber
Amber fossils are among the most fascinating natural artifacts, providing a unique window into the prehistoric past. These fossils are not typical stone fossils but are rather preserved organisms and organic material trapped within amber, which is fossilized tree resin. This guide delves into the formation, significance, types, and scientific value of amber fossils.
FORMATION OF AMBER FOSSILS
Resin Production: Amber begins as resin exuded by ancient trees, primarily conifers, as a natural defense mechanism against injury and insect infestation. This sticky substance can trap small organisms and plant material.
Fossilization Process: Over millions of years, the resin undergoes a series of chemical changes, known as polymerization, and becomes hard and stable. During this process, the trapped organic material is preserved in extraordinary detail.
Conditions for Fossilization: For resin to fossilize into amber, it must be buried and protected from environmental elements such as oxygen, which would otherwise cause it to decompose. Ideal conditions include rapid burial under sediment or water.
TYPES OF INCLUSIONS
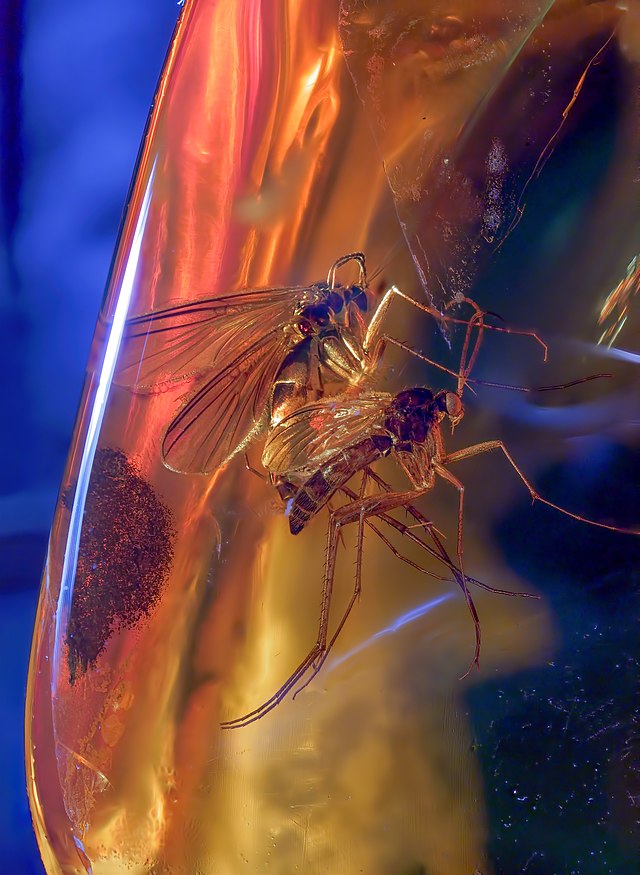
Insects: The most famous and scientifically valuable inclusions are insects. Amber can preserve a wide variety of insects in exquisite detail, including ants, mosquitoes, flies, and beetles. These inclusions provide insights into the diversity of ancient insect life.
Arachnids: Spiders and other arachnids are also commonly found in amber. These inclusions can show intricate details of their anatomy and behavior, such as web spinning.
Plant Material: Amber can contain pieces of ancient plants, including leaves, flowers, and seeds. These inclusions help scientists understand the flora of prehistoric environments.
Small Vertebrates: Although rare, small vertebrates such as lizards, frogs, and even feathers from birds have been found in amber. These fossils are exceptionally valuable for understanding ancient ecosystems.
Microorganisms: Amber can also preserve microorganisms like fungi, bacteria, and protozoa, offering a glimpse into the microscopic life of the past.
SCIENTIFIC SIGNIFICANCE
Paleontology: Amber fossils are invaluable to paleontologists because they preserve organisms in three dimensions and often in life-like poses. This level of preservation can reveal behaviors and ecological interactions that are not discernible in typical rock fossils.
Amber fossils are a remarkable natural phenomenon that offer a unique and detailed glimpse into prehistoric life. Their formation, diverse inclusions, and scientific value make them an essential subject of study in paleontology and other scientific fields. As technology advances and ethical considerations continue to shape their collection and study, amber fossils will remain a fascinating and valuable window into Earth’s distant past. Whether admired for their beauty, studied for their scientific insights, or valued for their historical significance, amber fossils are truly timeless treasures.