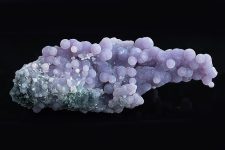
QUARTZ
VARIETIES OF QUARTZ

Macrocrystalline Varieties:
- Amethyst: Purple quartz used in jewelry and for metaphysical purposes.
- Citrine: Yellow to orange quartz, often used in jewelry.
- Rose Quartz: Pink quartz valued for its color and used in jewelry and decorative items.
- Smoky Quartz: Brown to black quartz used in jewelry and as a healing stone.
Cryptocrystalline Varieties:
- Chalcedony: A microcrystalline form of quartz, available in various colors and used in jewelry and carvings.
- Agate: Banded chalcedony with varying colors, often used in decorative items and jewelry.
- Jasper: Opaque quartz with impurities that give it various colors and patterns, used in carvings and jewelry
CHARACTERISTICS

Chemical Composition: Quartz is composed of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Color: Pure quartz, known as rock crystal, is colorless and transparent. However, impurities can give quartz a wide range of colors, resulting in varieties such as amethyst (purple), citrine (yellow), rose quartz (pink), and smoky quartz (brown).
Hardness: Quartz ranks 7 on the Mohs scale, making it a durable mineral suitable for various applications.
Crystal Structure: Quartz has a hexagonal crystal system and typically forms six-sided prisms ending in six-sided pyramids.
Transparency: Quartz can be transparent to opaque, with the level of transparency affecting its value and use.
HISTORY AND LORE
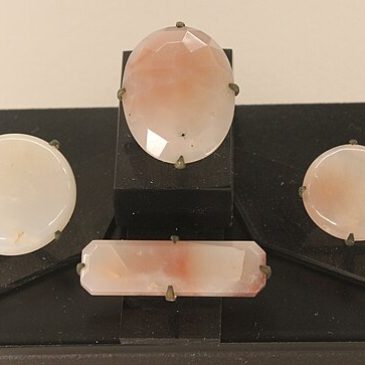
Ancient Uses: Quartz has been used since prehistoric times for tools, jewelry, and as a protective stone. Ancient cultures believed it had magical and healing properties.
Mythology and Folklore: In various cultures, quartz has been associated with spiritual and healing powers. For example, the ancient Greeks believed quartz was eternal ice sent by the gods.
Modern Significance: Today, quartz remains popular in jewelry and crystal healing. It is also crucial in various industrial applications due to its physical properties.
SOURCES

Geological Formation: Quartz forms in a variety of geological environments, including igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. It often crystallizes from silica-rich solutions in hydrothermal veins.
Major Sources: Quartz is found worldwide, with significant deposits in Brazil, Madagascar, the United States (Arkansas and California), Russia, and China. Brazil is known for producing large, high-quality crystals.
USES

Jewelry: Quartz is widely used in jewelry due to its variety of colors and affordability. It is often cut into faceted stones, cabochons, and beads.
Industrial Applications: Quartz is crucial in several industries:
- Glassmaking: Quartz sand is a primary ingredient in glass production.
- Electronics: Due to its piezoelectric properties, quartz is used in watches, clocks, radios, and other electronic devices.
- Construction: Quartz sand is used in concrete, mortar, and as a filler in various construction materials.
- Optics: High-purity quartz is used in optical instruments and lenses.
METAPHYSICAL PROPERTIES

Metaphysical Uses: Quartz is believed to have various healing and spiritual properties:
- Clear Quartz: Known as the “master healer,” it is thought to amplify energy and thought.
- Rose Quartz: Believed to promote love and emotional healing.
- Amethyst: Said to provide calmness and spiritual protection.
- Citrine: Associated with prosperity and success.